概述
AIDL是Android Interface Definition Language的简称,也就是Android接口定义语言,通过它我们可以定义进程间的通信接口。
实例
我们现在通过一个实例来介绍 AIDL 的使用方法。实例中服务端维护了一个Student列表,客户端可以通过跨进程调用来向列表添加和查询数据。
创建AIDL接口
AIDL文件支持的数据类型:
- 基本数据类型(int, long, boolean, float, double);
- String和CharSequence;
- List或Map类型:List或Map中的所有元素必须是AIDL支持的类型之一,或者是一个其他AIDL生成的接口,或者是定义的
parcelable。
如果我们需要使用非默认支持的数据类型,就要我们自己定义一个parcelable对象。
AIDL文件的创建方法如图所示:
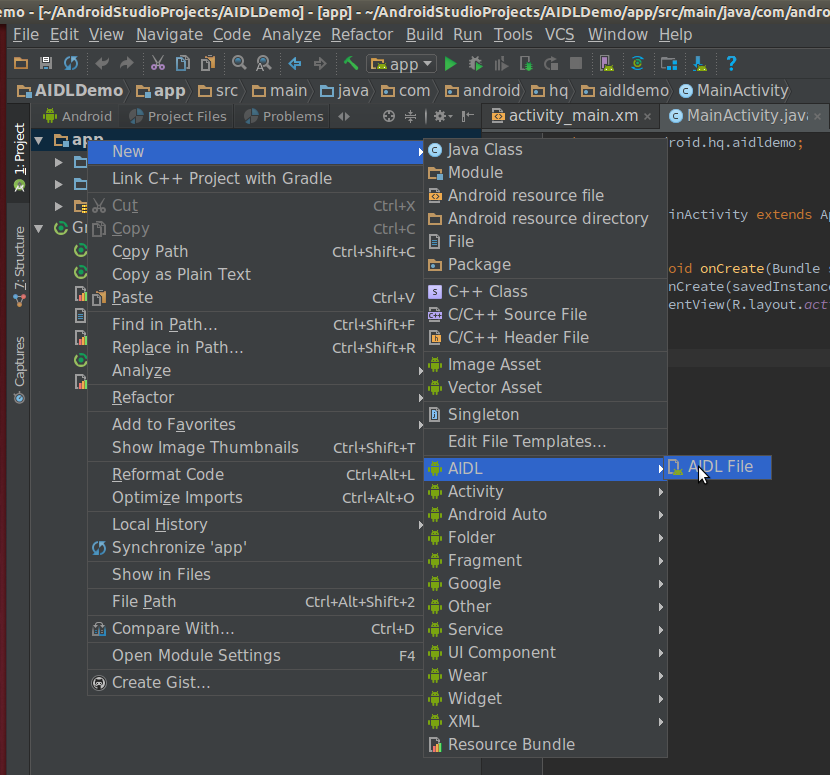
创建完AIDL文件,工程的目录会变成下图所示的样子,多了一个aidl包,和java在同一个层级之下。并且aidl文件的包和java文件的包是一样的。
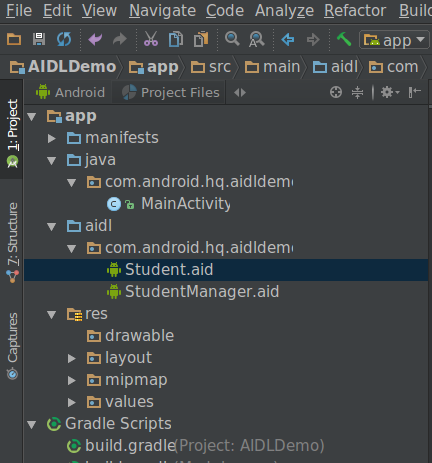
在这里有两个AIDL文件:
- Student.aidl:用来定义进程间需要传输的数据对象的parcelable类,以供其他AIDL文件使用AIDL中非默认支持的数据类型的。
- StudentManager.aidl:用来定义一些来完成跨进程通信的接口的类。
下面来看这两个接口的实现:
Student.aidl1
2
3package com.android.hq.aidldemo;
parcelable Student;
StudentManager.aidl1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9package com.android.hq.aidldemo;
import com.android.hq.aidldemo.Student;
interface StudentManager {
List<Student> getStudents();
//传参时除了Java基本类型以及String,CharSequence之外的类型,都需要在前面指定定向tag,具体加什么根据自己需要
void addStudent(inout Student student);
}
这里,虽然Studet.java和StudentManager.aidl在同一个包下面,但Studet不是系统默认支持的数据类型,使用的时候必须添加import进来。
Student.javaStudent是用于跨进程传输数据使用的,因此必须进行序列化,选择的序列化方式是实现 Parcelable 接口。
1 | public class Student implements Parcelable { |
在这里注意一下,我们知道如果是要在不同的应用中进行进程通信,两个应用必须要相同的 aidl 文件(包名也要一样)。或者是 Client 端 BookManager.aidl 定义的接口在 Service 端必须存在,即 Service 端的接口大于或等于 Client 端的接口。
这里为了方便移植,我们把进程通信需要的文件都放在 aidl 目录下面,当然也包括了 Student.java 这个java文件,但是Android Studio默认是只在src/main/java找源文件的,因此需要进行下面的配置,在 build.gradle 文件的android{}里面加上下面代码:
1 | sourceSets { |
添加之后编译,工程变成下图现实,aidl也就显示在源文件下面了:
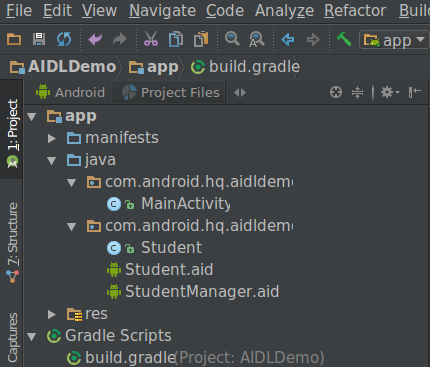
编译过之后,会生成下面的文件:
1 | app/build/generated/source/aidl/debug/com/android/hq/aidldemo/StudentManager.java |
StudentManager.aidl 这里void addStudent(inout Student student);的参数类型必须指定定向tag,否则编译会报下面的错误,这里我们指定的是inout类型。一旦申明为inout这个类型,Student类就必须实现readFromParcel()方法。具体inout类型介绍可以参考我的下一篇博客。
1 | 17:18:23.963 [ERROR] [org.gradle.api.Task] aidl E 8954 8954 type_namespace.cpp:130] In file /home/heqiang/AndroidStudioProjects/AIDLDemo/app/src/main/aidl/com/android/hq/aidldemo/StudentManager.aidl line 8 parameter student (argument 1): |
代码
AndroidManifest.xml
1 |
|
MainActivity.java
1 | public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { |
AIDLService.java
1 | public class AIDLService extends Service { |
结果
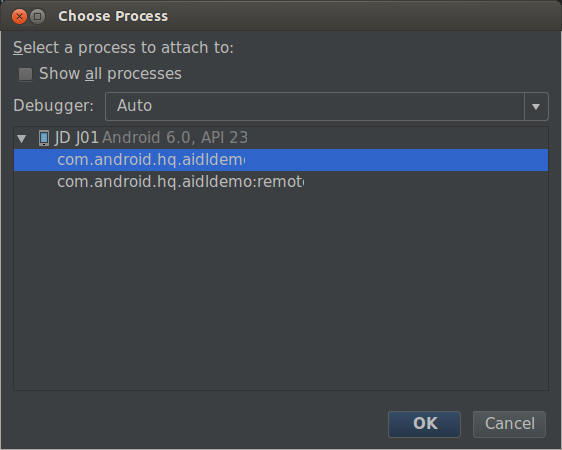
如图所示,Clent和Server是在两个不同的进程中的:
启动后分别点击添加和获取列表按钮,打印如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
906-08 19:30:10.047 10005 10005 D AIDLService: called onBind
06-08 19:30:10.072 10005 10017 D AIDLService: call getStudents(), student list is :[name = John, age = 6, grade = 1]
06-08 19:30:10.073 9991 9991 D Client : onServiceConnected. student list is : [name = John, age = 6, grade = 1]
06-08 19:32:51.814 9991 9991 D Client : addStudent : name = James, age = 7, grade = 2
06-08 19:32:51.815 10005 10016 D AIDLService: call addStudent(), student list is :[name = John, age = 6, grade = 1, name = James, age = 7, grade = 2]
06-08 19:33:09.875 10005 10017 D AIDLService: call getStudents(), student list is :[name = John, age = 6, grade = 1, name = James, age = 7, grade = 2]
06-08 19:33:09.876 9991 9991 D Client : getStudent. student list is : [name = John, age = 6, grade = 1, name = James, age = 7, grade = 2]
成功的进行了进程间通信。
问题
Android进程间通信是异步的还是同步的?
我们可以在程序中验证这个问题。
我们在AIDLService类的mStudentManager实现的方法addStudent()中添加一个延时:
1 |
|
我们在客户端调用addStudent()方法的结尾添加打印,这样可以得到函数调用结束的信息:
1 | public void addStudent(View view){ |
看到打印:1
2
3
406-08 19:42:28.505 20807 20807 D Client : addStudent : name = James, age = 7, grade = 2
06-08 19:42:28.506 20822 20833 D AIDLService: call addStudent(), student list is :[name = John, age = 6, grade = 1, name = James, age = 7, grade = 2]
06-08 19:42:30.506 20822 20833 D AIDLService: sleep end !
06-08 19:42:30.506 20807 20807 D Client : addStudent end
看到客户端等服务端调用完毕才会往下走,因此我们可以得到这样的结论:
Android进程间通信默认是同步的,这里为什么说默认呢?难道还有其他情况,是的,也可以是异步的,为什么呢?
看 StudentManager.java 中的 addStudent 方法:
1 | public void addStudent(com.android.hq.aidldemo.Student student) throws android.os.RemoteException |
再来看一下 IBinder 中对这个方法的介绍:
1 | /** |
flags 为0时是普通的RPC调用,为 FLAG_ONEWAY 时是 one-way RPC,是单向调用,执行后立即返回,无需等待Server端 transact() 返回。这个时候就是异步执行了。
具体如何实现异步调用请参考我的下一篇博客。
注意事项
Server 端 AIDL 文件升级问题
当我们把 AIDL 公开接口给外部第三方应用时,通常的做法是会将 AIDL 以及对应 Java 文件打包给第三方使用,这样做没有任何问题。但要注意的是在后续升级这个接口的时候,得保持接口中方法顺序不变,即只能在aidl的后面添加新方法,而不能在中间插入新方法。否则 Client 端后调用错乱导致调用不成功。
为什么呢?因为编译器会给我们自动根据 AILD 文件生成对应的 Java 文件,在这个 Java 文件中的 onTransact 方法中,自动为我们分配好了每一个方法的 code,这个code 的分配顺序是按照 AIDL 文件中的声明顺序来进行的,详细请看下面的代码。通过分析 android 进程间通信 binder 机制可以知道,则是客户端最后是通过调用 transact 方法,并传递这个 code 给 server 端,来完成调用。如果中间插入新的接口,会导致这个 code 错乱,调用的不是我们想要的方法。
1 | static final int TRANSACTION_testAIDL1 = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0); |
Client 和 Server AIDL 对应问题
从上面的分析得到一个结论,Client 端和 Server 端的 AIDL 可以不一致,Client 端的 AIDL 文件的接口可以是 Server 端的AILD 接口的一个子集,但这个子集必须是前面所有连续的接口的一个子集,方法顺序不能变。
另外,Client 端和 Server 端的 AIDL 的包名必须一致。
AIDL 接口不能重载
从上面的代码中可以看到,接口 code 的分配是根据方法名来分配的,没有涉及到参数,因此是不能重载的,如果重载的话编译是会报错的。